The best resolution for an industrial display depends on the application and viewing conditions. Here’s how to decide:
When Higher Resolution is Better
Detailed Visualization Required
- Used in medical imaging, precision engineering, or CAD applications.
- Example: Semiconductor manufacturing or quality inspection screens.
Large Screens with Close Viewing Distance
- If operators view the display up close, higher resolution improves readability.
- Example: Control rooms or complex monitoring dashboards.
High-End Image Processing or AI Applications
- Required for machine vision, automation, and AI-driven defect detection.
- Example: Smart factories using high-res cameras for real-time analysis.
When Lower Resolution is Enough (or Better!)
Far Viewing Distance
- If users see the screen from several meters away, extra resolution is wasted.
- Example: Factory status boards or warehouse inventory displays.
Power & Performance Efficiency
- Higher resolution requires more processing power and energy.
- Example: Outdoor signage and battery-operated devices.
Legacy System Compatibility
- Older systems may not support ultra-high resolutions.
- Example: Older industrial equipment interfaces.
Balanced Approach
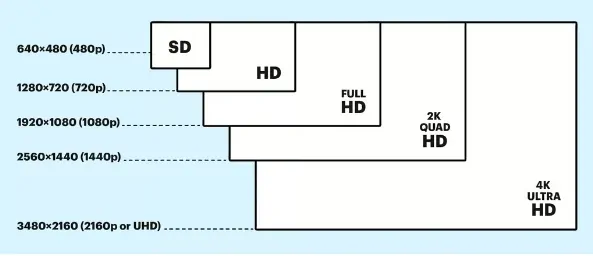
- 1080p (Full HD)– Standard for most industrial applications.
- 4K (Ultra HD)– Ideal for high-detail tasks but requires powerful GPUs.
- 720p or lower– Suitable for text-based interfaces or distant viewing.
LCD Displays & OLED Display product links for reference:
https://www.youritech.com/products/ips-displays/
